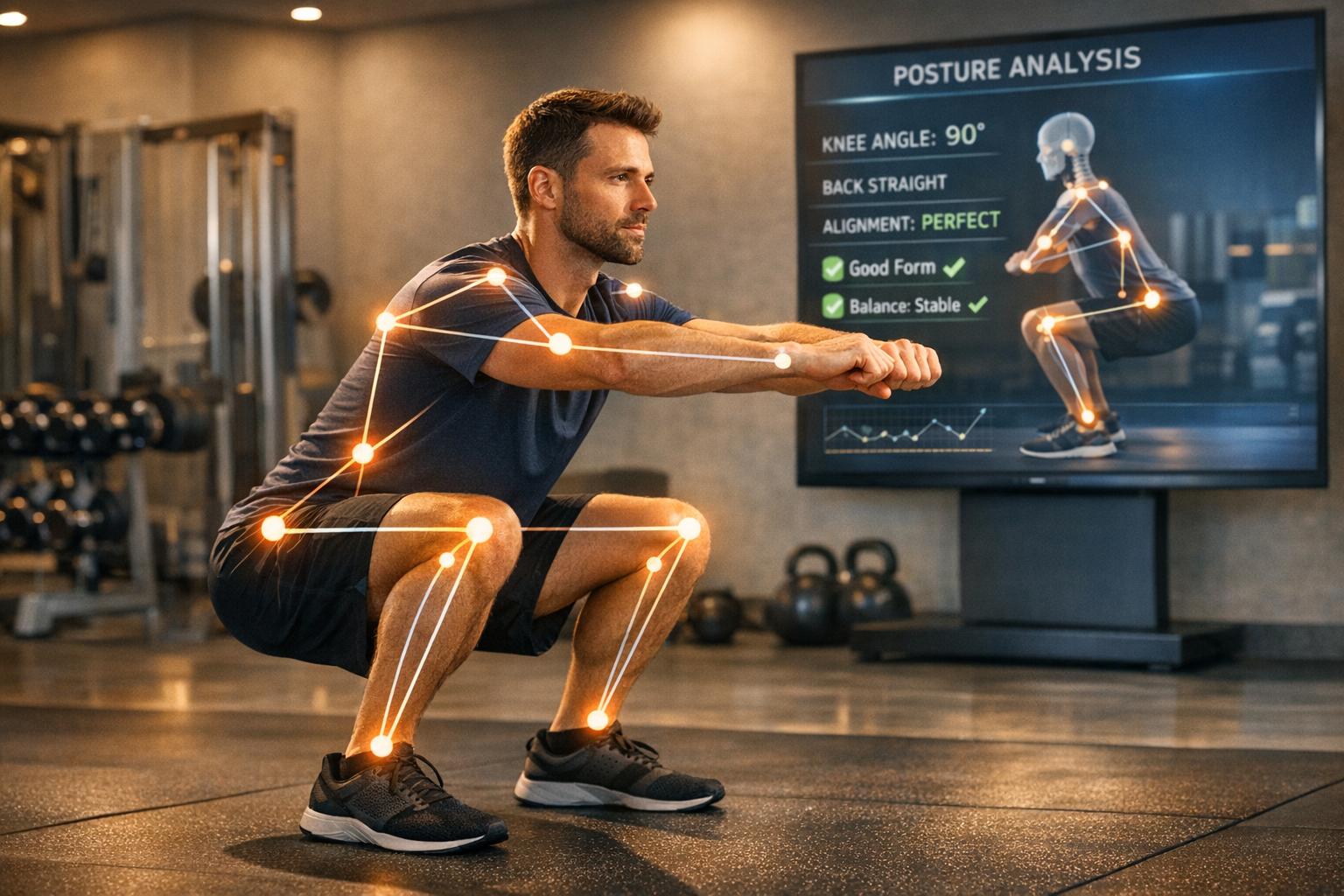

How AI Analyzes Posture in Real Time
AI is transforming the way people train by analyzing posture during workouts with remarkable precision. Using computer vision and pose estimation models, tools like CueForm AI track joint movements frame-by-frame, offering real-time feedback to prevent injuries and improve performance.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Why it matters: Poor form causes 60% of weightlifting injuries, especially for beginners without access to expert supervision.
- How it works: AI tracks body landmarks, calculates joint angles, and compares movements against biomechanical standards.
- What it does: Detects errors like knee collapse or uneven depth, provides corrections via visual cues, text, or audio, and validates reps based on proper technique.
- Results: Studies show a 20% decrease in injury risk and a 15% performance boost with AI-guided training.
AI tools like CueForm AI make expert-level coaching accessible to anyone with a smartphone, helping lifters train smarter and safer.
Creating Your Own AI Fitness Trainer: Analyzing Squats with MediaPipe
sbb-itb-c91a623
AI Technologies Behind Real-Time Posture Analysis
AI-driven posture analysis relies on advanced computer vision techniques, using just a standard smartphone camera - no fancy equipment needed. These methods form the backbone of detailed movement tracking and analysis.
Pose Estimation Models
Pose estimation models are the heart of real-time posture tracking, mapping your body’s position from video input. Popular models like MediaPipe BlazePose, OpenPose, and YOLOv7-pose work through a two-step process: first, they identify the region of interest, then they mark key body landmarks.
MediaPipe's BlazePose stands out for fitness applications, thanks to its ability to track 33 3D landmarks. This includes not just major joints like shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles but also hands and feet - far surpassing the 17 points tracked by standard COCO-based models [4]. This detailed mapping is essential for analyzing complex movements like squats or deadlifts. Plus, BlazePose is optimized to run efficiently on mobile devices, delivering real-time performance on phone CPUs and even faster speeds on mobile GPUs [4].
BlazePose achieves its speed by using the face to estimate the body’s center, rotation, and scale [4]. This clever shortcut allows for rapid video processing, enabling instant feedback during workouts.
Keypoint Detection and Movement Analysis
After identifying body landmarks, the AI calculates joint angles - for example, the angle between the hip, knee, and ankle during a squat. To ensure accuracy, these angles are adjusted based on torso length (the distance from neck to hips), which accounts for variations in body size and camera distance [6][5]. The exercise is then broken into phases - often labeled as Normal, Transition, and Pass - based on specific joint angle thresholds [3]. If the system detects issues like knee collapse or back rounding, it flags these errors in real time.
This precise measurement is what powers platforms like CueForm AI. By leveraging these methods, they provide personalized, actionable feedback to help users correct their form during strength training sessions.
How AI Processes Video for Posture Feedback
Once the AI pinpoints your body’s key landmarks, it analyzes this data across multiple video frames to assess your overall movement. This involves examining individual frames, tracking patterns over time, and dividing your exercise into distinct phases for a detailed review.
Frame-by-Frame Analysis
AI processes 30–60 video frames per second, calculating joint angles in real time to evaluate your movement mechanics. After identifying key points like your shoulders, hips, and knees, the system determines joint angles. For example, during a squat, it measures the angle between your hip, knee, and ankle to assess depth and alignment.
Pose estimation technology achieves joint angle measurements with an accuracy of 3 to 5 degrees when compared to laboratory-grade motion capture systems [7]. This level of precision allows the AI to catch issues such as knee valgus or spinal flexion as they occur, rather than identifying them after the fact.
The system then compiles these frame-level insights to uncover broader movement patterns.
Analyzing Movement Patterns Over Time
Looking at frames individually only provides part of the picture - the AI also examines how your body moves through space over the entire exercise. By tracking key point coordinates over time, the system generates a continuously updating 3D map of your movement cycle [7]. This temporal analysis captures patterns that single frames can’t, such as uneven tempo or imbalances in movement.
For instance, the AI can identify a "stripper squat" by analyzing the hip-to-shoulder rise ratio during the ascent phase [1]. If your hips rise faster than your shoulders, the system highlights this imbalance. It also monitors tempo consistency, measuring the time from the start of your descent to the lockout phase for each rep. If the coefficient of variation exceeds 25%, it signals fatigue and raises an alert [1].
"Tempo control is one of the first things to go when athletes fatigue, but it's also one of the hardest things to coach in a team setting. The AI catches this objectively."
- Zach Lush, Certified Functional Strength Coach, SportSensAI [1]
Rep Counting and Phase Detection
Beyond tracking movement, the AI ensures the quality of your exercises by segmenting reps and phases. It doesn’t just count reps - it validates them against biomechanical standards. A rep only counts if it meets specific criteria, such as hitting the proper depth or maintaining correct joint alignment [7]. The system identifies exercise phases by monitoring the velocity and direction of body segments. For example, in a squat, it detects the "bottom" position when the vertical velocity of your hips pauses before reversing direction. Similarly, for a bicep curl, the AI counts a rep when the angle between your upper arm and forearm reaches a minimum threshold and then returns to the starting position [6].
Using these methods, platforms like CueForm AI break down lifts into setup, descent, transition, and ascent phases, offering detailed, phase-specific feedback. This ensures you only get credit for reps that meet proper movement standards, giving you more accurate and actionable insights.
How AI Delivers Personalized Posture Corrections
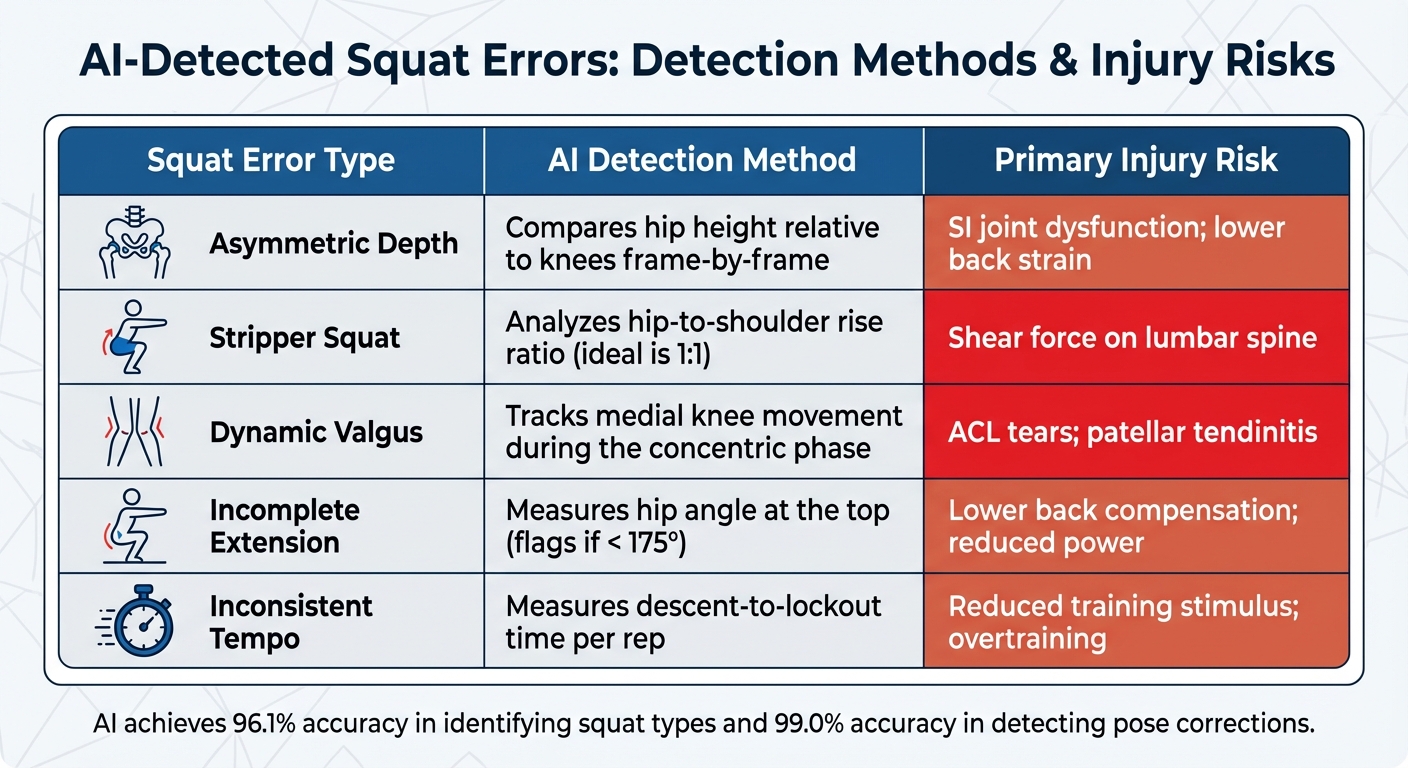
Common Squat Form Errors Detected by AI and Associated Injury Risks
AI takes joint angles and movement patterns and transforms them into precise, actionable corrections in real time. It identifies the exact form issues, delivers adjustments in multiple formats, and tailors recommendations to fit your body mechanics and training goals.
Detecting Form Errors and Posture Problems
AI compares your movement data to biomechanical benchmarks set by experts to identify specific form issues. For instance, during a squat, it checks if your knee flexion angle stays within the standard range of 113 ± 7 degrees [2]. If your movement falls outside this range, the system flags the issue and categorizes the error.
AI can catch mistakes that even experienced coaches might miss. Using Bi-CGRU models, these systems achieve a 96.1% accuracy rate in identifying squat types and 99.0% accuracy in detecting pose corrections [2]. By analyzing movement sequences, they can identify errors that only occur during certain phases of an exercise.
| Squat Error Type | AI Detection Method | Primary Injury Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Asymmetric Depth | Compares hip height relative to knees frame-by-frame | SI joint dysfunction; lower back strain |
| Stripper Squat | Analyzes hip-to-shoulder rise ratio (ideal is 1:1) | Shear force on lumbar spine |
| Dynamic Valgus | Tracks medial knee movement during the concentric phase | ACL tears; patellar tendinitis |
| Incomplete Extension | Measures hip angle at the top (flags if < 175°) | Lower back compensation; reduced power |
| Inconsistent Tempo | Measures descent-to-lockout time per rep | Reduced training stimulus; overtraining |
The system adjusts these thresholds to suit individual body mechanics. For example, someone with long femurs and a short torso may naturally lean forward more during a squat, which wouldn’t necessarily be flagged as incorrect [2].
Delivering Feedback Through Multiple Formats
AI platforms provide corrections using visual overlays, text prompts, and audio cues, offering real-time guidance. Visual feedback often includes colored joint markers - red for incorrect positioning and green for correct - paired with on-screen text and neutral spine indicators [8].
One study showcased how a deadlift posture system, powered by BlazePose, tracked 33 keypoints and delivered multimodal feedback at 24–30 fps on standard mobile devices [8].
Audio feedback, enabled by text-to-speech technology, allows you to adjust your form without needing to glance at a screen. Verbal cues like "Lift hips higher" help you stay focused during intense sets [8][9].
Platforms like CueForm AI combine these feedback methods. By analyzing your uploaded exercise videos, they provide detailed written feedback with actionable cues for your next session. They also feature a conversational AI coach, so you can ask follow-up questions and receive guidance tailored to your goals and movement patterns.
"AI provides instant feedback on exercise form and performance, automatically adjusting workout intensity and routines to maximize results and prevent injuries."
- Bill Davis, CEO, ABC Fitness [9]
This variety of feedback not only corrects immediate errors but also helps you build better habits for long-term improvements.
Benefits of AI Coaching for Lifters
AI-driven feedback reduces injury risk, enhances performance, and improves technique over time by offering consistent and objective analysis that evolves with your progress. Studies show that training programs using machine learning assessments result in a 20% decrease in injury rates and a 15% boost in performance compared to traditional coaching methods [1].
AI tracks your technique over time, spotting early signs of fatigue or compensatory patterns that could lead to overuse injuries [10]. It also distinguishes between technical mistakes and physical limitations. For example, if the system repeatedly flags heel lift during squats, it might suggest ankle mobility drills instead of just highlighting the error [1]. By identifying the root cause of movement issues, you can address them more effectively.
"It's like having an assistant coach who never gets tired and never misses a rep."
- Zach Lush, CFSC, Co-founder of SportSensAI [1]
AI also adapts its form requirements based on your training style. For instance, squat depth standards vary between powerlifting (hip crease below the knee) and Olympic weightlifting (full depth with hamstrings touching calves) [1]. By specifying your goals, the AI ensures your technique is evaluated against the right criteria, avoiding generic assessments that don’t align with your objectives.
Accuracy and Testing of AI Posture Analysis
Measured Improvements in Exercise Form
A study conducted by Seoul National University in September 2023 revealed how effective AI coaching can be in improving exercise form. Participants who used an AI coaching app showed a significant improvement in their squat posture scores - from 0.20 to 8.00 - over two weeks. In contrast, the control group saw no progress[13]. These participants trained for 30 minutes, five days a week, and their left knee angle improved from 75.06° to 63.13°, showcasing better squat mechanics.
The accuracy of these systems heavily relies on the technology behind them. Deep learning models have demonstrated impressive results, with some studies reporting posture classification accuracy as high as 99.0%[2]. However, there are still limitations. A randomized controlled trial published in Nature Scientific Reports (September 2021) highlighted that while the AI achieved 84.0% sensitivity in identifying correct squats, it only managed 27.6% specificity in detecting incorrect form, leading to an overall accuracy of 56.5% compared to expert evaluations[11].
Despite these advancements, detecting subtle errors remains a challenge. In one validation test involving 200 videos, an AI system achieved an 80% agreement rate with expert human coaches. While this is close to the 85–90% inter-rater reliability typically seen among human evaluators, it underscores the room for improvement[1].
User Testing and Continuous Improvement
AI platforms are constantly evolving by comparing their feedback with expert human evaluations. By analyzing performance data from thousands of sessions, developers identify areas where the AI might overcorrect or miss errors, adjusting algorithms to enhance precision[11].
Platforms like CueForm AI employ this feedback loop to refine their analysis. By tracking user performance over time, these systems can distinguish between isolated mistakes and recurring movement patterns, ensuring feedback that feels tailored and precise.
"The AI is a tool, not a replacement for coaching judgment. I've seen it flag 'excessive forward lean' on an athlete with long femurs who's squatting perfectly fine for their body. That's where the human coach steps in."
- Zach Lush, Certified Functional Strength Coach, Co-founder of SportSensAI[1]
A major step forward in this field is the shift from coordinate-based pose estimation to vision-language models. These newer systems are better equipped to handle issues like camera angle dependency and joint occlusion[1]. By analyzing movement conceptually, they can provide accurate feedback even when parts of the body are obscured. As more users interact with these platforms and upload videos, the systems continue to refine their capabilities, closing the gap between AI and expert human coaching. This ongoing evolution ensures that AI feedback becomes increasingly reliable and effective.
Conclusion
AI-powered posture analysis is reshaping strength training. By identifying risky patterns like spinal flexion, knee valgus collapse, and uneven loading before they cause harm, this technology acts as a safeguard against the form-related injuries that account for 60% of weightlifting injuries among high school athletes[1]. Beyond injury prevention, it enhances performance by promoting proper muscle engagement and efficient movement, delivering a 15% boost in performance gains when compared to traditional coaching alone[1]. This marks a major step toward data-driven and accessible coaching solutions.
What’s even more exciting is how accessible this technology has become. Tools like CueForm AI now bring professional-grade feedback straight to your smartphone, offering 24/7 guidance on exercises like squats, bench presses, and deadlifts. This means expert-level coaching is no longer reserved for those who can afford pricey personal trainers - it’s available to anyone with a smartphone.
The measurable feedback provided by these platforms is a game-changer. With objective scores ranging from 0 to 100, technique becomes a tangible metric you can track alongside your progress in weight and reps. Users report a 10% improvement in technique after just 10 sets, with long-term gains climbing to 34% - and for beginners, improvements can reach as high as 47%[12].
This technology doesn’t just help individuals; it also supports coaches. By scaling their ability to deliver precise, consistent feedback, AI allows a single coach to effectively guide more athletes without compromising quality.
Whether you’re just starting out and learning basic movement patterns or you’re a seasoned lifter chasing new personal records, AI-driven posture analysis offers the instant, objective insights needed to train smarter, safer, and more effectively. As this technology continues to advance, its role in reducing injuries and boosting performance is already undeniable.
FAQs
How does AI provide accurate posture analysis compared to a human coach?
AI uses cutting-edge algorithms and machine learning to deliver precise posture analysis, offering an objective look at movement. By breaking down video frames, it pinpoints key body landmarks, measures joint angles, and compares them against a vast database of expertly labeled examples. This enables the AI to catch even the smallest form issues that might escape the notice of seasoned coaches.
Platforms like CueForm AI push this even further by providing real-time, tailored feedback for exercises like squats, bench presses, and deadlifts. The system highlights exact details, such as “knee valgus exceeds 5 degrees” or “hip hinge is 2 inches shallow,” so users can make on-the-spot corrections. Unlike human observation, AI offers consistent, tireless analysis for every single rep, helping to lower injury risks and refine technique.
What are the benefits of using AI for real-time posture correction during workouts?
AI-powered posture correction offers real-time feedback to help you maintain proper form during workouts. By analyzing joint angles and movement patterns as you move, these systems can pinpoint misalignments instantly, helping you avoid injuries like knee, back, or hip strain. This immediate feedback lets you correct your technique on the spot, encouraging better movement habits and boosting strength gains more efficiently.
Platforms such as CueForm AI make this technology easy to access and budget-friendly, with personalized coaching available 24/7 for about $10 a month. These tools automatically monitor key metrics like depth, symmetry, and knee alignment, giving you detailed insights and tracking your progress - all without needing pricey equipment or in-person trainers. The blend of accuracy, safety, and affordability empowers users to stay consistent and reach their fitness goals more effectively.
Can AI provide personalized feedback based on my body type and fitness goals?
Yes, AI can personalize its feedback to match your specific body type and fitness goals. By evaluating details such as your physique, fitness level, and training targets, it offers customized guidance to refine your form and boost performance. For instance, CueForm AI employs this method to deliver real-time, tailored advice, helping you work out efficiently while minimizing the risk of injury.
Related Blog Posts
Plans
Choose the plan that best fits your needs.
Free
Try it out
Starter
Perfect for fitness enthusiasts