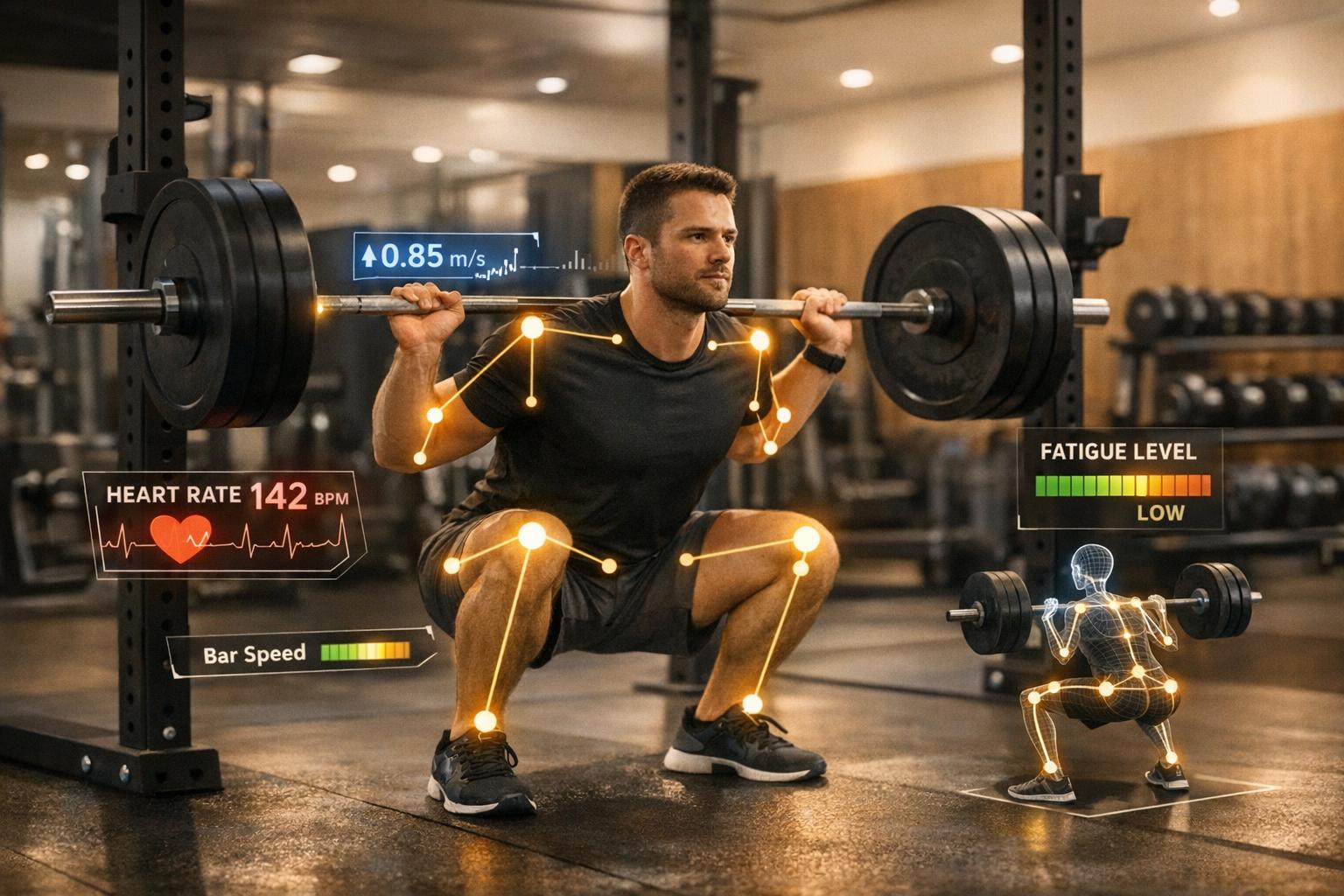

Real-Time Fatigue Tracking with AI: How It Works
Real-time fatigue tracking with AI helps you train smarter by monitoring your physical, mental, and cognitive performance during workouts. By analyzing metrics like bar speed, joint angles, heart rate, and movement patterns, AI provides instant feedback to optimize your training, prevent injuries, and improve results. Here's how it works:
- AI Tools in Action: Systems use cameras or wearable sensors to measure bar speed, movement efficiency, and technique changes in real time.
- Fatigue Detection: Metrics like velocity loss (e.g., a 20% drop in bar speed) signal when you're approaching fatigue and should adjust weight or stop a set.
- Form Monitoring: AI tracks joint alignment and movement patterns, flagging issues like knee valgus or reduced range of motion before they lead to injury.
- Personalized Adjustments: By combining external (bar speed) and internal (heart rate, muscle activity) data, AI tailors training intensity to your readiness.
AI-powered fatigue tracking eliminates guesswork, helping you train effectively while staying safe. Whether you're lifting for strength, power, or hypertrophy, these tools ensure every rep counts toward your goals.
Data Sources for AI Fatigue Tracking
Bar Speed and Velocity Loss
AI systems measure bar speed - how fast the barbell moves during each repetition - in meters per second (m/s, roughly 3.28 ft/s). This metric is a direct way to gauge neuromuscular fatigue. As your muscles tire and produce less force, the bar slows down.
Using tools like computer vision systems (e.g., Detectron2), modern AI tracks the movement of Olympic plate center points in video frames. By applying homography transformations - calibrated using the plate's diameter - AI converts 2D video data into real-world speed metrics [12][14].
Velocity loss (VL) is a key indicator here. It measures the percentage drop in bar speed from your fastest repetition (usually the first or second) to your current one. For instance, if your first squat rep moves at 1.0 m/s and by the fifth rep the speed drops to 0.8 m/s, that's a 20% velocity loss. Research suggests that a 20% velocity loss often indicates you've completed about half of your potential reps before failure, while a 40–50% loss signals you're nearing full muscle fatigue [15].
To ensure accurate tracking, set up a stable tripod-mounted camera at a side angle (0º–25º) with good lighting and contrast to minimize errors [13].
These velocity metrics lay the groundwork for more detailed analysis of movement changes as fatigue progresses.
Repetition Performance and Technique Changes
AI systems also monitor your form, analyzing kinematic data like joint angles, 3D movement patterns, and bar path to detect technique breakdowns caused by fatigue. This is done using depth cameras or wearable IMUs.
When fatigue sets in, noticeable changes can occur: squat depth may decrease, the bar path might drift, and knees could collapse inward. AI models pick up on these shifts by analyzing features such as the Root Mean Square (RMS) of energy signals and the Zero Crossing Rate (ZCR) of flexion torque, which can reveal increased muscle tremors [11]. Force plates further contribute by measuring Center of Pressure (COP) displacement. Greater postural sway, for example, can signal fatigue even before you miss a rep [8].
One study demonstrated that deep learning models leveraging IMU and force plate data achieved a 94% correlation with self-reported fatigue levels during complex exercises [8].
Together with these mechanical metrics, physiological data provides even more comprehensive insights into fatigue.
Wearable and Physiological Data
Wearable devices bring another layer of analysis by tracking how your body internally responds to physical exertion. While bar speed reflects external performance, physiological signals like heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) reveal cardiovascular stress and recovery status of the autonomic nervous system [9]. Surface electromyography (sEMG) sensors, on the other hand, monitor muscle activity. Fatigue is often marked by an increase in RMS amplitude and a decrease in Median Frequency [11].
Combining motion data with physiological signals through multi-modal fusion enhances precision. For example, hybrid systems that pair wearable devices with RF sensing and process the data using AI algorithms have achieved 100% accuracy in detecting fatigue [7]. This is critical because the same external workload - like five sets of squats at 225 lbs - can produce vastly different internal responses depending on factors such as recovery, sleep, and stress levels.
"Taking physiological signals as indicators of fatigue enables objective, real-time fatigue monitoring at the individual level."
– Neusa R. Adão Martins et al. [9]
Unlike subjective measures like RPE (Rate of Perceived Exertion), which can be influenced by mood or motivation, physiological data offers an objective, reliable baseline that’s harder to skew.
How AI Models Analyze Fatigue in Real Time
Data Capture and Preprocessing
AI systems monitor movement data through two primary methods: computer vision and wearable sensors. Computer vision, often using tools like Microsoft Azure Kinect, tracks 3D skeletal positions without requiring markers. On the other hand, wearable sensors, such as 6-axis Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), measure acceleration and rotation at specific points on the body [1][3].
Once collected, the raw data undergoes cleaning and standardization. The AI then converts absolute positions into relative coordinates by subtracting the hip position from other joint positions. This step ensures the system functions consistently, regardless of factors like height, body size, or camera placement [1]. To further refine the data, the AI segments continuous movement into individual repetitions. This is achieved using peak-finding algorithms that track joints like the pelvis or ResNet-based models that identify rep boundaries [1][3]. These preprocessing steps are critical for ensuring that fatigue predictions are both precise and personalized. The cleaned, segmented data becomes the foundation for accurate fatigue analysis.
Feature Extraction and Pattern Recognition
After preprocessing, the AI focuses on extracting features that indicate fatigue. These features include joint angles, velocity, range of motion (ROM), and statistical markers like variance and skewness [1][16]. For instance, the system might notice a reduction in squat depth by 3 inches or detect that a bar path is drifting forward compared to earlier reps.
Machine learning models, such as Gradient Boosting Regression Trees, analyze these features to predict both external metrics (e.g., power output) and internal ones (e.g., Rating of Perceived Exertion, or RPE). Studies reveal that these models can predict RPE with a mean absolute percentage error of just 8.08% [1]. Additionally, a single wrist-mounted IMU can identify when you're nearing failure (with two or fewer reps left) with an F1 score of 0.82 [3].
"Fatigue can be comprehensively quantified by the external and internal load, where the external load is the work done by the athlete, and the internal load is the psychological and physiological response." – Bert Arnrich [1]
Real-Time Feedback and Training Adjustments
Once the AI extracts features and identifies patterns, it delivers immediate training guidance. The system processes data rapidly, with inferences taking as little as 23.5 milliseconds [3]. Based on the analysis, it provides real-time recommendations - such as reducing the load when velocity slows, stopping a set at your fatigue threshold, or increasing rest intervals if form begins to break down.
Some adaptive resistance systems go a step further by employing motorized digital resistance. These systems automatically adjust the load or tempo during a set based on your force output [16]. This dynamic adjustment ensures you're training at an appropriate intensity while avoiding excessive fatigue that could compromise form or increase injury risk. The key advantage is that these insights and adjustments occur during the workout, allowing you to make immediate changes before fatigue leads to mistakes or harm.
BodyPark Atom: Training Alone Was Holding Me Back Until I Tried This AI Fitness Device

sbb-itb-c91a623
Using Real-Time Fatigue Tracking in Your Training
Velocity Loss Thresholds by Training Goal for AI Fatigue Tracking
Setting Up Video Recording for Lifts
Proper camera placement is crucial for accurate AI fatigue tracking. For squats and deadlifts, position the camera at waist height, and for overhead movements, set it at chest height. Use a sturdy tripod to keep the camera stable. Record in HD resolution at 60 fps - avoid 4K, cinematic modes, or slow-motion settings, as these can slow processing or distort data [13]. Handheld recording should also be avoided since any camera motion can throw off the AI's ability to track movement and velocity accurately [13].
Make sure the athlete, barbell, and plates remain fully visible throughout the set, from setup to racking. To help the AI process data efficiently, create a high-contrast environment between the weight plates and the background. Avoid positioning bright lights behind you or near the barbell, as glare can interfere with tracking. If your gym is dimly lit, consider using lighter-colored plates or adjusting the camera angle for better visibility [13]. For iOS users, devices like the iPhone 11 or newer are recommended for handling real-time computer vision tasks without lag [13].
Once you’ve ensured accurate video capture, the next step is to set fatigue thresholds that align with your training objectives.
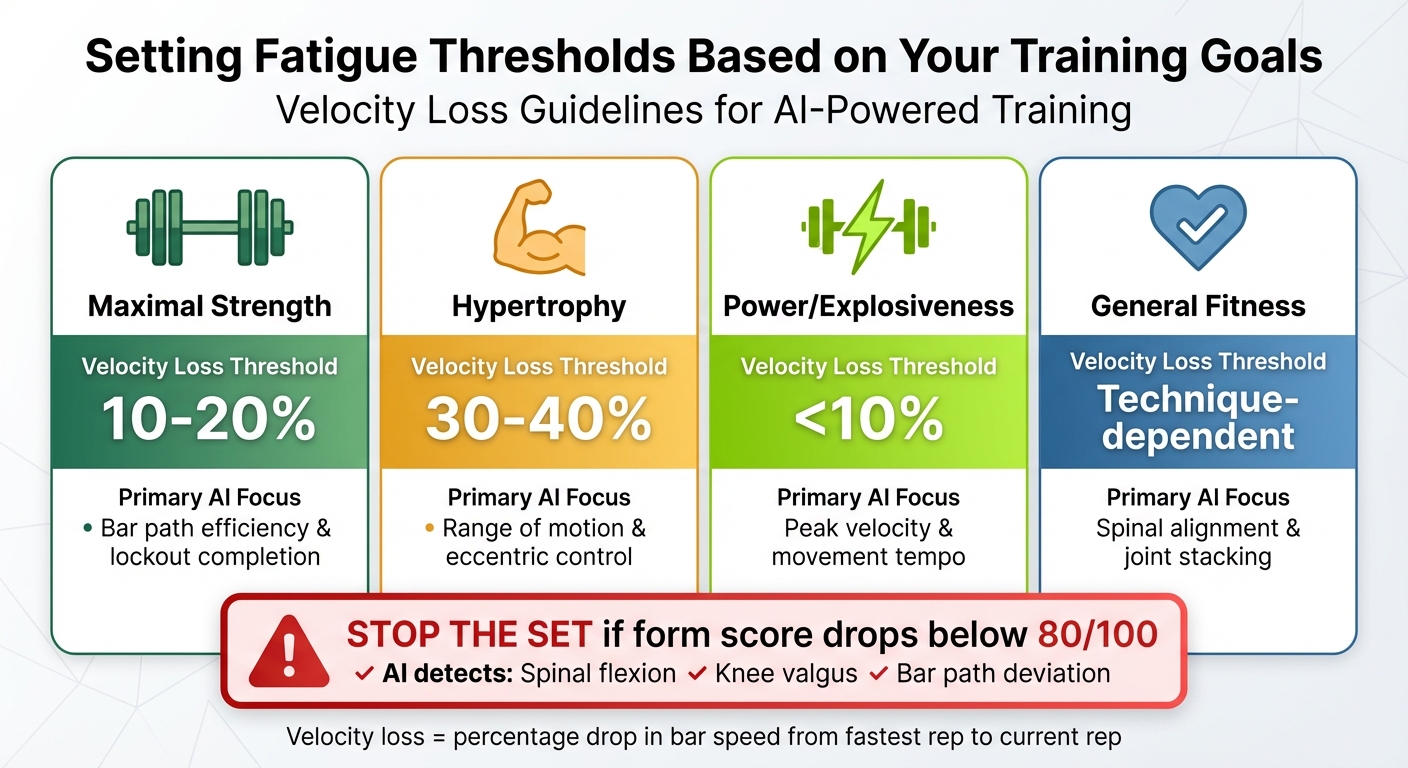
Setting Fatigue Thresholds Based on Your Goals
Your fatigue thresholds should align with what you're aiming to achieve in your training. Velocity loss is one of the earliest signs of fatigue, often appearing before a noticeable drop in strength [17]. For building maximal strength and power, aim for a low velocity loss threshold of 10–20%, ensuring every rep remains explosive. If your focus is hypertrophy, a higher threshold of 30–40% allows for greater metabolic stress and proximity to muscle failure [17].
| Training Goal | Velocity Loss Threshold | Primary AI Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Maximal Strength | 10% - 20% | Bar path efficiency & lockout completion |
| Hypertrophy | 30% - 40% | Range of motion & eccentric control |
| Power/Explosiveness | < 10% | Peak velocity & movement tempo |
| General Fitness | Technique-dependent | Spinal alignment & joint stacking |
Regardless of your goal, stop the set if your form score drops below 80/100. The AI can detect fatigue-related issues like excessive spinal flexion, knee valgus, or deviations in the bar path, all of which could increase injury risk [2][18].
Adjusting Training Variables Based on Feedback
When the AI detects a drop in velocity during your working sets, it’s a clear sign to reduce the load [17]. For example, if you’re aiming for three sets of eight reps but find yourself completing 6, 4, then 2 reps at the same weight, your fatigue levels are too high for productive training [17]. The AI provides real-time data, taking the guesswork out of when to adjust.
Rest intervals should also adapt based on your heart rate recovery. If your heart rate remains elevated for longer than usual, it may indicate chronic fatigue, suggesting the need for extended rest periods or even a deload week [17]. Additionally, if the AI consistently flags technique issues, it might be time to swap out complex compound lifts for simpler variations until your coordination improves [17]. These adjustments are made during your workout, allowing you to stay on track without waiting to review training logs days later.
Using CueForm AI to Track Technique-Based Fatigue
How CueForm AI Detects Technique Changes Under Fatigue
CueForm AI takes fatigue tracking to another level by using advanced pose estimation technology. With just your smartphone camera, the system monitors 17–33 specific body keypoints - like your shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles - at a smooth 30–60 fps rate [19]. This real-time tracking calculates joint angles and compares them to biomechanical models optimized for movements like squats, bench presses, and deadlifts [18][19][20].
As fatigue sets in, the AI identifies subtle changes in form, such as knees caving inward (valgus collapse), a rounded spine, reduced squat depth, incomplete lockouts, or shifts in movement speed and rhythm [2][18][19]. Impressively, modern pose estimation models achieve joint angle accuracy within 3–5 degrees of lab-grade motion capture equipment [19].
| Analysis Dimension | Fatigue Indicators Detected by AI |
|---|---|
| Joint Alignment | Knee valgus (caving), loss of neutral spine [18][19] |
| Range of Motion | Reduced squat depth, partial lockouts, incomplete reps [18][19] |
| Temporal Patterns | Slower movement speed, inconsistent rep tempo [18][19] |
| Symmetry | Left-right imbalances in movement or loading [19] |
| Postural Control | Sagging hips in planks, spinal flexion in deadlifts [18][19] |
CueForm AI assigns each lift a score from 0 to 100, highlighting exactly when your form begins to break down [2][18]. It can also be set to count only the reps that meet strict technical standards, ensuring every repetition contributes meaningfully to your progress [19]. This level of precision provides actionable insights for improving your technique.
Using CueForm AI Feedback to Adjust Your Training
CueForm AI doesn’t just track your performance - it helps you make immediate adjustments. If your technique score drops during a session, the system provides real-time feedback to help you correct it on the spot [2][18]. This feedback comes in various forms, such as visual overlays, audio cues like “Drive through your heels,” and detailed post-set breakdowns [19][21].
"Fatigue indicators such as slower movement velocity or inconsistent form are early warning signs of potential injury. Monitoring these metrics in real time allows coaches to intervene before athletes push beyond safe limits." - Perch.fit [21]
Use the post-set analysis to identify the exact point at which your form starts slipping. For example, if your scores consistently drop at higher rep ranges or under heavier loads, it might be time to reduce intensity or volume for that exercise [19][21]. By tracking these trends over time, you can make smarter decisions about when to deload or focus on recovery. Research shows that prioritizing proper movement patterns can cut injury risk by 23% to 50% [19].
Getting Personalized Feedback with the AI Coach
CueForm AI also features an interactive AI coach that provides tailored advice based on your training data [20]. After each session, you can ask the AI coach specific questions about your performance - like why certain technique issues occurred or how to fix them - and get actionable recommendations. This conversational tool not only helps you understand what went wrong but also guides you toward better form and smarter programming decisions going forward.
Safety, Limitations, and Best Practices
Understanding AI Model Limitations
AI fatigue tracking has its flaws. Factors like poor lighting, cluttered backgrounds, or moving objects can confuse camera-based sensors, leading to inaccurate readings [1][4]. Single-camera setups, in particular, may struggle with self-occlusion during complex movements, where parts of your body can get blocked from view [1][4].
To get a clearer picture of your fatigue, combine AI insights with how you feel physically. AI models often miss psychological and emotional factors that influence your sense of tiredness. If the AI says you're fine but you feel off, trust your instincts. On the flip side, if the system flags a technique issue while you're feeling great, take that feedback seriously. Many AI systems rely on binary classifications, which means they often detect problems only after they've already occurred [5].
These limitations highlight the importance of actively managing fatigue to avoid injuries.
Managing Fatigue and Injury Risks
Ignoring fatigue signs and pushing through poor form can significantly increase your risk of injury. While real-time AI feedback can be a game-changer, it’s how you respond to that feedback that truly ensures safer training.
Pay attention to specific danger signals flagged by AI systems, like excessive spinal flexion (which could lead to disc injuries), knee valgus collapse (which stresses the ACL/MCL), or shoulder impingement during pressing exercises [2]. If your AI tool, such as CueForm AI, flags these issues, immediately reduce the load or stop the set altogether. Set clear boundaries before your workout - for instance, decide to stop if your technique score drops below 70 out of 100 or if you notice a significant decrease in movement speed [2].
Implementation Tips for Your Training Environment
To minimize the impact of AI limitations and lower your injury risk, follow these best practices in your training setup.
Ensure your camera captures your entire body clearly, with proper lighting and minimal background distractions, as discussed in earlier sections [4]. Before starting your session, double-check that all equipment and sensors are functioning correctly. Wearable sensors should have good skin contact, and cameras should be positioned to avoid obstructions from gym equipment [10][4].
Don’t rely on a single metric like bar speed or heart rate to assess fatigue. Instead, track multiple data points. Combine external load metrics, such as power output and bar speed, with internal ones like heart rate, perceived exertion, and technique quality [1][6]. This layered approach allows you to spot signs of fatigue early, keeping your training both effective and safe.
FAQs
How does AI identify and differentiate between physical and internal fatigue during workouts?
AI differentiates between physical fatigue and internal fatigue by analyzing various data collected during a workout. Physical fatigue refers to external factors like power output, force, and motion patterns, while internal fatigue focuses on the body’s responses, such as heart rate, muscle activity, and perceived exertion levels.
To make this distinction, AI combines data from wearables and video analysis. Wearables capture internal metrics like heart rate and muscle signals, while video-based tools assess physical effort by examining movement and force. Machine learning models process these data streams, identifying patterns that enable AI to classify and track both types of fatigue effectively.
CueForm AI leverages this approach by analyzing workout videos alongside wearable data to deliver tailored feedback. It can identify when internal fatigue rises more quickly than physical performance, guiding users to adjust their technique or take breaks. This helps improve performance while minimizing the risk of injury.
How can I set up my camera for accurate AI fatigue tracking during strength training?
To get accurate results from AI fatigue tracking, start by optimizing your camera setup. Use a high-resolution camera - ideally at least 1080p at 30 fps - and place it on a stable surface like a tripod to minimize any shaking. Position the camera about 6–8 feet away, ensuring your entire body and the bar path are fully visible. For movements like squats or deadlifts, a side view works best, while a front view is useful for checking symmetry.
Lighting plays a big role too. Go for evenly distributed, shadow-free lighting and avoid placing bright windows or direct sunlight behind you, as this can interfere with tracking. Keep the background clean and free of clutter or anything moving, which might distract the AI. Before diving into your workout, do a few test reps to make sure the AI is tracking your movements correctly. If needed, tweak the angle or distance to improve accuracy.
How does AI help adjust training intensity and reduce the risk of injuries?
AI technology evaluates your movements in real time, comparing them to biomechanical models designed to highlight potential issues like excessive knee wobble or a rounded back. CueForm AI, for instance, uses your phone's camera to track joint angles and bar paths. It flags technique problems that could increase your risk of injury, such as improper alignment or posture. By measuring these deviations, it also estimates the strain on your muscles and joints, offering insights to help you adjust your form for safer workouts.
AI also leverages velocity-based training (VBT) to fine-tune workout intensity. By tracking bar speed - say, 0.30 m/s during strength-focused sets - it can identify fatigue when speed slows by roughly 20%. Based on this data, the system might recommend lowering the weight to avoid overtraining and ensure you stay in the ideal performance range.
Beyond this, AI can even gauge internal fatigue markers, such as perceived exertion, by analyzing your movement patterns. By combining form analysis, speed tracking, and fatigue metrics, it delivers real-time feedback to help you train smarter while reducing the chances of injury.
Related Blog Posts
Plans
Choose the plan that best fits your needs.
Free
Try it out
Starter
Perfect for fitness enthusiasts